- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Greek
- German
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Socket Weld Flange Dimensions and Pressure Ratings
Jan 6 2026
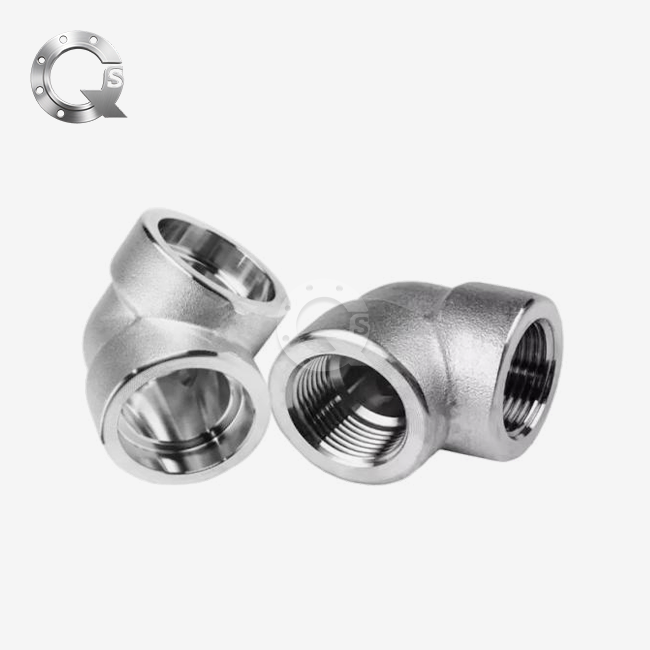
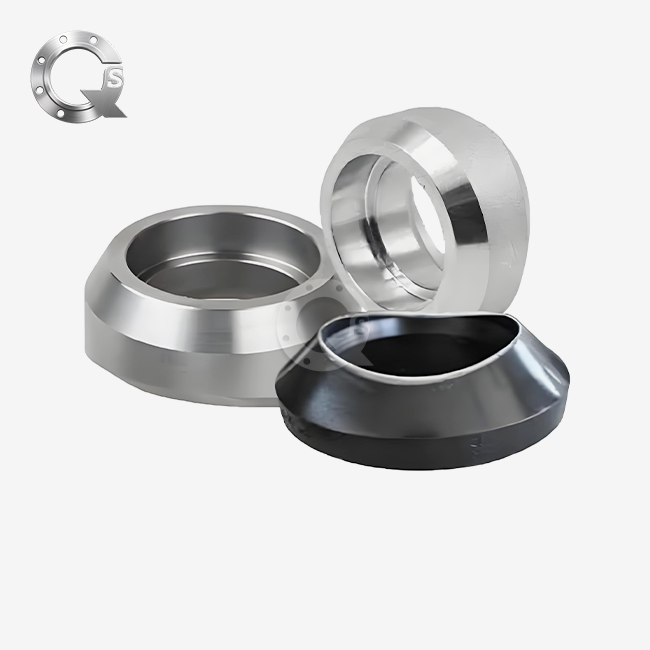
Understanding SW socket weld flanges specs is very important for project success when choosing pipe parts for important industrial uses. These special flanges are needed for oil and gas pipes, power plants, and chemical processing plants because they are accurate in size and can withstand high pressures. Because of their unique socket design, socket weld flanges offer better joint integrity. They do this by providing excellent structural support while keeping links leak-proof in harsh working conditions. Their standard sizes and pressure levels make sure that they can be used in a wide range of commercial systems around the world.
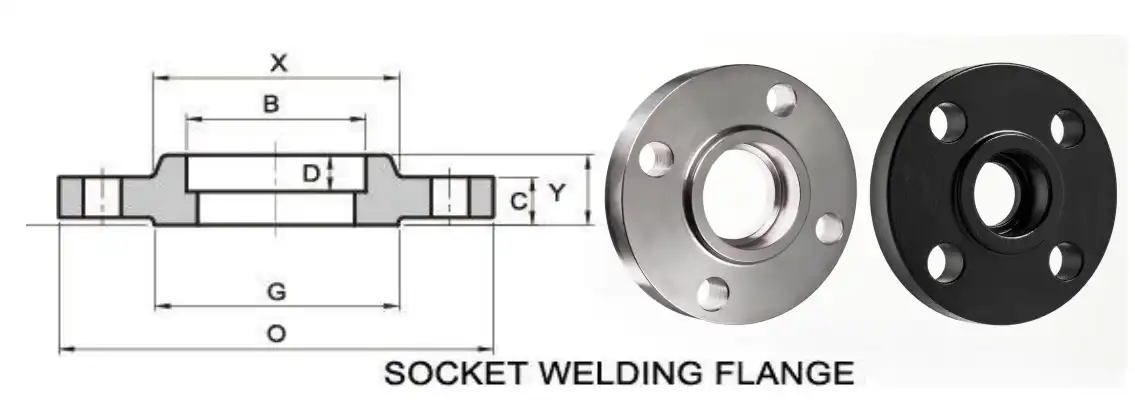
Understanding Socket Weld Flange Dimensions
Socket weld plate sizes are based on standards that are known all over the world. For North American uses, ASME B16.5 and ASME B16.47 are the main standards to follow. These standards set important size limits that make sure the new pipes fit in perfectly with the ones that are already in place.
Key Dimensional Parameters
The basic sizes of socket weld flanges include a number of important measures that have a direct effect on how well they fit and how well they work in use. The thickness of the flange depends on the pressure class. For higher pressure levels, the material needs to be thicker to handle the forces of operation. Specifications for the hub diameter make sure that the socket is the right depth for the best weld entry, and the specifications for the hole make sure that the pipe's outer diameter fits with the right amount of space.
The bolt circle width is another important measurement that determines how far apart and where on the ring edge the bolt holes are placed. This measurement is directly related to pressure class ratings, since uses with higher pressure need bigger bolt rounds to spread the mechanical loads out properly. Because of how these measurements relate to each other, a balanced design is made that is both strong and easy to make.
Standardized Size Ranges
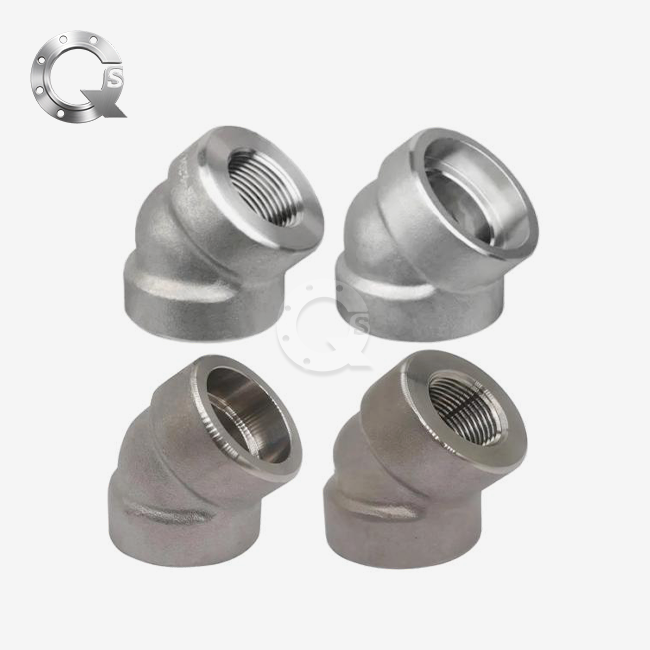
Manufacturers make socket weld flanges in sizes from ½" to 60", so they can meet the needs of a wide range of businesses. Smaller diameters are used for monitoring and control systems, while bigger diameters support the main process lines in chemical plants and factories. Each size increase follows a standard development pattern. This makes sure that it works with standard pipe plans and makes it easier for buying teams to keep track of supplies.
For bigger flange sizes, the standards for dimensional error get stricter. This shows how important dimensional accuracy is in high-pressure uses. Precision in manufacturing has a direct effect on how well the seal seats, how evenly the bolts are loaded, and how well the joint holds together in normal use.
Face Type Configurations
Socket weld flanges can work with different face shapes, such as raised face (RF), flat face (FF), and ring type joint (RTJ). Each type of face meets different closing needs based on pressure levels and the fit of the gasket material. When used with spiral wound or compressed fiber gaskets, RF faces offer effective sealing for mild pressure uses. On the other hand, RTJ configurations work best in high pressure settings that need metal-to-metal sealing.
Pressure Ratings for Socket Weld Flanges
The operating range for socket weld flanges is set by their pressure ratings, which also set safe working limits for different temperature situations. The ASME pressure classes, which go from Class 150 to Class 2500, give standard rates that are based on certain design pressures and temperature ranges.
ASME Pressure Classification System
Based on the qualities of the material and construction factors, the ASME pressure class method sets the maximum working pressure. Class 150 flanges can usually handle pressures of up to 285 psi at room temperature, while Class 2500 setups can handle pressures of over 6,170 psi at the same temperature. As working temps rise, these scores go down accordingly, which shows that the material's strength goes down at high temperatures.
For choosing the right plate for high-temperature uses like steam systems and heat processing equipment, it's important to know how pressure and temperature relate to each other. The ASME standards' pressure rating charts give detailed information on how to find safe working limits for a wide range of temperatures.
Material Impact on Pressure Capabilities
The choice of material has a big effect on how well socket weld flanges can handle pressure. When it comes to normal uses, carbon steels like ASTM A105 are very strong, while stainless steels like A182 F304 and F316 are more resistant to rust while still having similar pressure ratings. Specialty metals, such as duplex stainless steels (F51, F53, and F55), have better strength qualities that allow them to handle higher pressures in tough settings.
For uses in low temperatures, certain materials are needed, such as A350 LF2, which keeps its mechanical qualities at temperatures below zero while still being able to handle pressure. The method of material certification makes sure that the material can be tracked and meets quality standards. These are important for pressure tank uses that need recorded material features.
Testing and Validation Protocols
Before installing a flange, it is usually tested hydrostatically at 1.5 times the design pressure as part of pressure testing methods. These tests make sure that the structure is solid and look for any flaws that might make it unsafe to use. In addition to pressure testing, ultrasonic testing and penetrant checking are also used to make sure the quality of important uses.
Comparing Socket Weld Flanges with Other Flange Types
Because they are different from other joining ways, socket weld flanges are a special case within the flange family. Knowing these differences helps you make smart choices about which to use based on the needs of your program.
Socket Weld vs. Weld Neck Flanges
Socket weld flanges are easier to install than weld neck designs because you don't have to prepare and cut the pipe ends precisely. The hole design places the pipe automatically at the right depth for placement, which cuts down on installation mistakes and makes the weld more consistent. But weld neck flanges work better in high-pressure situations because the curved hub shape makes them better at distributing stress.
Furthermore, fatigue resistance is a key difference, with socket weld flanges performing exceptionally well in mild cycle situations. The socket design makes the change from pipe to flange smooth, which reduces stress builds up that could cause wear problems over time.
Advantages Over Threaded Connections
Socket weld flanges get rid of the chance that a threaded link will come loose when the temperature changes. The soldered joint makes a solid connection that stays strong for the whole life of the equipment. When compared to socket weld designs, threading lowers the effective wall thickness at the joining point, which limits the amount of pressure that can be applied.
With SW socket weld flanges, you can be more sure of the quality of the installation because the welding process lets you check for damage without damaging the parts. Threaded connections depend on the right amount of assembly force and thread contact, which can be very different depending on how the connection is made and the conditions of the surroundings.
Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
Socket weld flange joints work best and last the longest when they are installed correctly. Following set processes reduces the chance of mistakes during installation and increases the dependability of operations.
Pre-Installation Preparation
For a socket weld flange fitting to go well, both the flange and the pipe must be properly prepared. To get straight, burr-free areas on the ends of pipes that make socket placement easier, they need to be cut correctly. Socket hole checking makes sure that the dimensions are correct and that there are no flaws that could make the fit less snug.
Positive material identification (PMI) checks the suitability of the materials used for the flange and the pipe. This stops galvanic rust problems from happening in service. Cleaning methods get rid of oil, industrial leftovers, and other contaminants that could hurt the quality of the weld or cause service issues.
Welding Procedures and Quality Control
When you repair a socket joint, you have to follow certain steps because of the way the socket joint is shaped. The right electrode choice, welding settings, and method make sure that the metal completely fuses without adding too much heat, which could warp the joint or cause problems with the metal's structure.
The space between the pipe end and socket bottom is very important because it lets the metal expand and contract during welding and keeps stress from building up at the weld toe. This gap usually measures 1/16" and must be kept the same throughout the welding process. A direct check and penetrant testing done after the welding process confirms the soundness of the weld and finds any problems that need to be fixed.
Maintenance and Inspection Requirements
Regular inspections help find problems before they become serious, and visual inspections focus on areas that are likely to fatigue crack, especially around the weld toe area where stress naturally builds up. Ultrasonic thickness measurements keep an eye on material loss from corrosion or erosion, especially in harsh service environments.
Visually checking for signs of corrosion or damage on bolts is part of bolt inspection, as is checking the torque to make sure the gasket is properly loaded. Gasket condition assessment finds wear and tear that could cause leaks, and flange face inspection finds damage that could stop the seal from working properly. These preventative maintenance methods increase service life and reduce unplanned downtime.

Procurement Considerations for Global B2B Clients
To strategically buy socket weld flanges, you need to look at the supplier's skills, quality systems, and how reliable their supply chain is. Good buying strategies balance cost with quality needs and make sure deliveries happen on time to meet project deadlines.
Supplier Qualification Criteria
The first step in choosing a supplier is to check their quality certifications, such as ISO 9001 quality management systems and industry-specific approvals like API 6A for oil and gas applications. The next step is to evaluate their manufacturing capability, which includes their production capacity, the sophistication of their equipment, and their technical know-how to handle complex specifications or special requests.
When evaluating quality control systems, the focus is on the inspection methods, testing capabilities, and documentation practices that make sure the quality of the products is always the same. Suppliers must show that they have the ability to trace materials, non-destructive testing resources, and calibrated measuring equipment to meet the strict quality requirements that are common in critical applications.
Cost Optimization Strategies
To effectively manage costs, you need to know the different things that affect the price of socket weld flanges. For example, the price of materials changes depending on the alloy and the market, and the difficulty of making them rises with size, pressure rating, and special features. However, buying in bulk can often lead to big cost savings, especially for standard configurations.
Logistics costs, inventory carrying costs, and possible failure costs for socket weld flanges are all part of the total cost of ownership. Finding the right balance between these factors requires a close look at quality levels, delivery reliability, and supplier support capabilities. Forming strategic partnerships with qualified suppliers can save you money while also ensuring consistent quality and supply continuity.
Technical Specification Management
Misunderstandings about technical requirements can lead to wrong products or delivery delays if they are not communicated clearly. Detailed specifications should include dimensional requirements, material specifications, pressure ratings, face types, and any special testing or certification requirements. Standard references like ASME B16.5 provide common technical language that makes it easier to get accurate quotes and lowers specification errors.
Specification clarity is very important for custom requirements because changes to standard designs can have a big effect on cost and delivery time. Working together with suppliers to develop specifications often leads to cost-effective alternatives that meet functional requirements while making production easier.
QinSteel: Your Premier SW Socket Weld Flanges Manufacturer
As a world leader in the manufacturing of piping components, QinSteel specializes in producing high-quality socket weld flanges that meet the strict needs of critical industrial applications. Our wide range of manufacturing capabilities allows us to make flanges with diameters from ½" to 60" and pressure ratings from Class 150 to Class 2500, making sure that all industry requirements are met.
Advanced Manufacturing Excellence
Our modern production facilities have precision machining centers and automated quality control systems that keep dimensional tolerances within ±0.1mm. This level of accuracy in manufacturing guarantees perfect alignment and the best sealing performance in tough environments. Each flange goes through a full dimensional inspection using coordinate measuring machines and is pressure tested at 1.5 times the rated pressure to make sure the structure is strong.
The range of materials includes carbon steel grades like ASTM A105 and A350 LF2, stainless steel alloys like A182 F304 and F316, and specialty duplex grades F51, F53, and F55. Material traceability systems keep track of each heat from the time it is certified at the mill until it is delivered to the customer. This gives full documentation for pressure vessel applications and regulatory compliance needs.
Quality Assurance and Certifications
QinSteel has a number of quality certifications, such as ISO 9001 quality management systems and industry-specific approvals like API 6A and PED compliance. Our quality control laboratory tests every production lot for positive material identification (PMI), ultrasonic testing, and dimensional verification. These strict quality controls make sure that all of our product lines perform consistently and reliably.
Non-destructive testing options include ultrasonic checking of the integrity of the weld, penetrant testing for surface flaws, and magnetic particle testing for important uses. Mill test certificates are sent with every shipment, showing all the material properties and traceability information needed to meet code requirements.
Global Supply Chain Solutions
Our logistics network offers a range of shipping options, such as EXW, FOB, and DDP terms, to make international purchasing easier. Specialized packaging and anti-corrosion coatings protect flanges while they're in transit, and we can also offer expedited shipping for projects that need to be done quickly. Strategic inventory management allows for quick delivery of standard configurations, and 70% of orders ship within 48 hours.
Custom engineering services help with specific project needs by working together to create specifications and test prototypes. OEM and ODM options allow for custom sizes, materials, or performance needs while still meeting our quality standards and delivery promises.
Conclusion
Understanding SW socket weld flanges dimensions and pressure ratings is important for making sure that piping systems work well in a wide range of industrial settings. Purchasing professionals can choose the best parts that meet performance needs and stick to a budget thanks to the standardized dimensional systems set up by ASME and other international organizations. Choosing the right materials, installing them correctly, and keeping them in good shape can extend their useful life and lower operational risks. Strategic supplier partnerships with qualified manufacturers like QinSteel give you access to technical expertise, quality products, and reliable supply chain solutions that are necessary for project success.
FAQs
What rules control the sizes of socket weld flanges?
These standards make sure that socket weld flanges from different makers and areas can be used interchangeably. In North America, they are set by ASME B16.5, B16.36, and B16.47, while in Europe, they are set by EN 1092-1.
How do pressure values link to the materials used for flanges?
Material properties directly affect how much pressure a material can handle. Stainless steel grades usually have a higher pressure tolerance than carbon steel grades. Specialty alloys like duplex stainless steels offer better strength for high-pressure applications while still being resistant to corrosion.
How much space should there be between the pipe end and the hole bottom?
The normal gap is 1/16" (1.6 mm) wide and allows for heat expansion during welding while keeping stress from building up at the weld toe. For the best joint stability, this gap must be kept the same throughout the welding process.
Can socket weld flanges be used for jobs that involve high temperatures?
When suitably sized for the temperature, socket weld flanges work well in high-temperature situations. Following the ASME pressure-temperature charts that show safe working limits for different material types, pressure numbers go down as temperature rises.
Contact QinSteel for Premium SW Socket Weld Flanges
Precision-engineered SW socket weld flanges from QinSteel can meet the needs of your pipe system and go above and beyond industry standards. Our wide range of products comes in sizes from ½" to 60" and can withstand pressures up to Class 2500. They are made from high-quality materials like A105, A182 F304/F316, and special duplex metals. We are a reliable provider of SW socket weld flanges and offer full expert support, unique planning services, and on-time shipping plans that help you keep your projects on track. Get in touch with our technical team at info@sxqinsteel.com to talk about your unique needs and find out how our knowledge can help you save time and money on buying while also ensuring high performance and dependability.

References
ASME B16.5-2020, Pipe Flanges and Flanged Fittings: NPS 1/2 through NPS 24 Metric/Inch Standard, American Society of Mechanical Engineers, New York, 2020.
Harvey, John F., "Pressure Vessel Design: Nuclear and Chemical Applications," Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, Third Edition, 1991.
Bickford, John H., "An Introduction to the Design and Behavior of Bolted Joints," Marcel Dekker Inc., Fourth Edition, 2008.
Brown, William M., "Piping Design and Engineering," Gulf Professional Publishing, Second Edition, 2017.
Singh, Karan P., "Mechanical Design of Heat Exchangers and Pressure Vessel Components," Arcturus Publishers, 2004.
Ellison, Tony, "Process Plant Layout and Piping Design," Gulf Professional Publishing, First Edition, 2018.
Learn about our latest products and discounts through SMS or email



